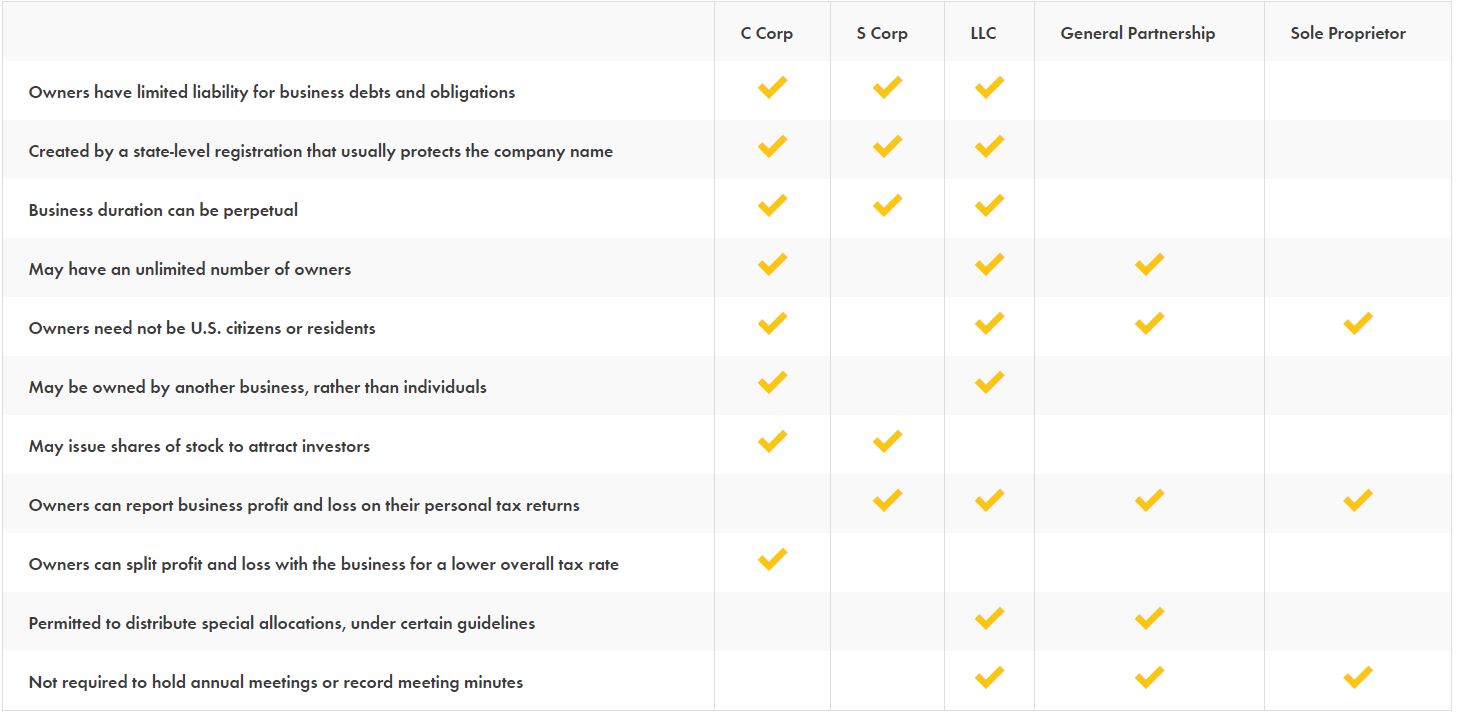
What is a Corporation (Inc)?
Description
A corporation is a separate legal entity that exists independently from its owners. A corporation is created and comes into existence when articles of incorporation (charter or certificate of incorporation in certain states) are filed with the proscribed fees, and accepted by the proper state authority.
Structure
A corporation is owned by stockholders. While stockholders do not directly manage the corporation, they influence corporate decisions through indirect actions such as electing and removing directors, approving or disapproving amendments to the articles of incorporation and voting on important corporate decisions.
The members of the Board of Directors are responsible for managing the affairs of the corporation. Usually, directors make only major business decisions, however they supervise and appoint officers who make the
day-to-day business decisions of the corporation.
Officers are responsible for the everyday management of the corporation.
Typically, officers are appointed directly by the Board of Directors.
A stockholder may serve on the Board of Directors and also be an officer of the corporation. In fact, in most states one person is enough to form a corporation, and that person can be the sole officer, director and stockholder.
Advantages
The most important advantage of incorporation is that it gives its stockholders limited liability. Since the corporation is a separate legal entity, its stockholders are protected from the debts and liabilities of the corporation. Other advantages include:
- A corporation has unlimited life.
- If an owner dies or sells his interest, the corporation will continue to exist.
- Ability to easily establish insurance and retirement plans.
- Ownership of a corporation is easily sold or transferred through sale or transfer of stock.
- Capital can be raised through the sale of stock.
- A corporation has centralized management that may remain in place after a sale.
Limitations
The primary disadvantage to incorporation is the possibility of double taxation. The profits of a corporation are taxed twice when the profits are distributed to shareholders as dividends. They are taxed first as income to the corporation, then second as income to the shareholder. However, all reasonable business expenses such as salaries and other operating expenses are deductions against corporate income that can minimize double taxation. “Double taxation” can be eliminated by making an S Corporation election.
Management
- A corporation is owned by stockholders. While stockholders do not directly manage the corporation, they influence corporate decisions through indirect actions such as electing and removing directors, approving or disapproving amendments to the articles of incorporation and voting on important corporate decisions.
- The members of the Board of Directors are responsible for managing the affairs of the corporation. Usually, directors make only major business decisions, however they supervise and appoint officers who make the day-to-day business decisions of the corporation.
- Officers are responsible for the everyday management of the corporation. Typically, officers are appointed directly by the Board of Directors.